Antonio Damasio’s Somatic Marker Hypothesis
The somatic marking hypothesis has been one of the most influential theories in the field of neuroscience. In it, he delves into the influence that emotions can have on the decision-making process.
The neurologist and physician Antonio Damasio is the one who proposed this hypothesis, rejecting the one proposed by Descartes. In this way, it is understood that the human being is a complex organism that acts conditioned by a wide range of factors.
The origins of the somatic marker hypothesis
Antonio Damasio, a physician and neurologist, published in 1994 a book called El error de Descartes. In this book, the somatic marker hypothesis was first upheld, arguing that decision-making depends on or is guided by homeostatic changes in the body. According to Damasio, this means that the sudden physical changes that the body generates lessen the burden of the rationalization process.
The somatic marker hypothesis broke with mind-body dualism. That is, it ended with the idea that the brain is a different, or just as differentiated, part of the body. Regarding the decisions that are made, Damasio highlights the value of experience. Thus, in similar circumstances, the person is likely to repeat the strategies with which he was successful.

How are somatic markers manifested?
According to Damasio, somatic markers can manifest themselves, for example, through sweating, increased heart rate, agitation, abdominal pain, etc. This reaction of the organism occurs in the absence of physical effort or universal stressor potential in the environment. In this sense, these reactions are contemplated by the presence of some type of emotion or reminiscence associated with an emotion.
It is as if the organism reacts in the presence of some kind of non-existent danger. That is, without the presence of a real threat, the body reacts in the same way as if danger were present, preparing the individual for the most typical responses (fight or flight).
Primary and secondary inducers in the somatic marker hypothesis
Somatic markers can be generated from two events: primary inducers and secondary inducers. Primary inducers are stimuli of innate origin or acquired through learning. Thus, if a stimulus appears to induce an innate or acquired response through learning, an emotional response will take place around it.
Secondary inducers, however, are those stimuli that are evoked from personal or hypothetical memory. That is to say, remembering or imagining a situation that will provoke a response based on how agreeable it is.
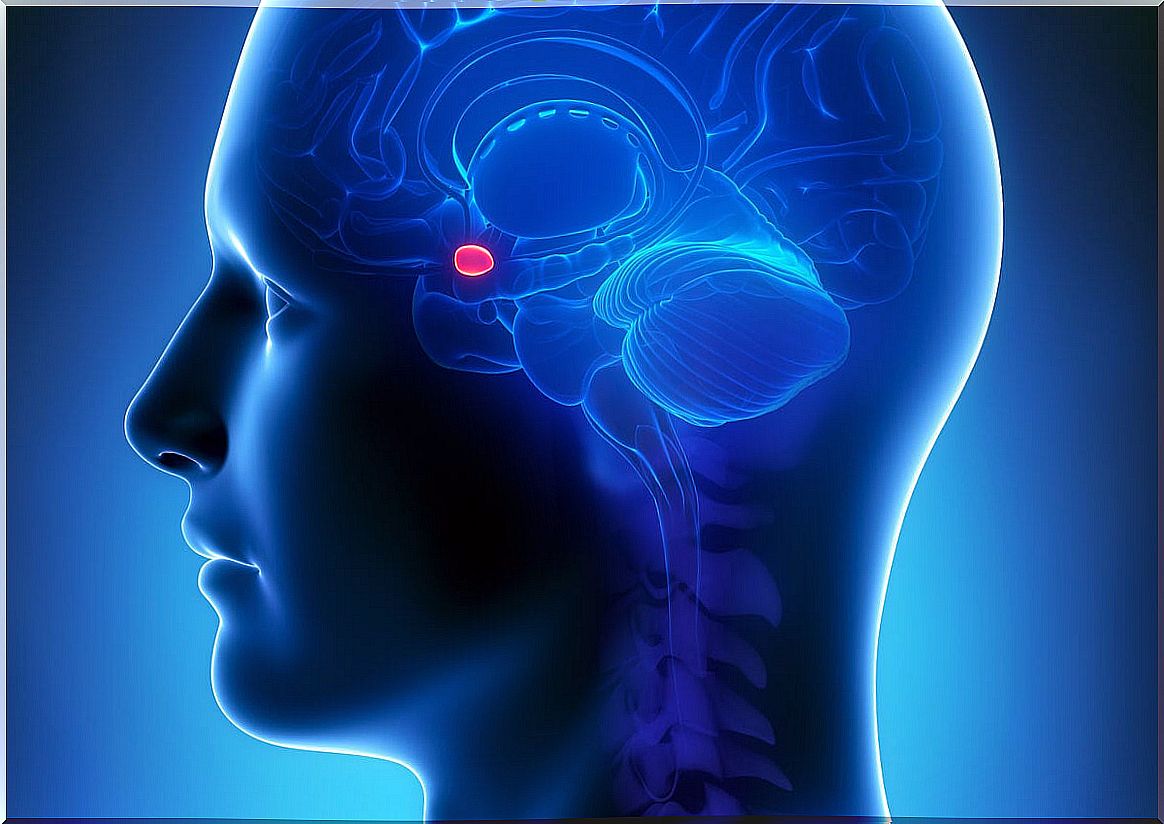
The role of the amygdala and other brain regions
According to the model and the primary and secondary inducers, the amygdala constitutes the key factor in the somatic marker hypothesis. It is the region through which the primary inducers are processed, triggering emotional signals, which are generated at the level of the hypothalamus and brain stem.
In this way, some affective states and certain learning patterns are consolidated, giving rise to the appearance of secondary inducers. The orbitofrontal cortex is the main responsible for the generation of somatic markers associated with the primary inducer.
Is the somatic marker hypothesis related to decision making?
According to the model of the somatic marker hypothesis, decision making can be guided by emotions. Thus, there must be a link between the ability to experience and perceive emotions and the ability to make adaptive decisions.
Decision-making processes are complex mechanisms. It has been seen that individuals with learning difficulties, people with addictive disorders or with brain injuries, show more difficulties in making decisions.
The somatic marker hypothesis has not been without criticism. In this sense, it has been investigated whether the somatic marker hypothesis is really necessary in the decision-making process. In one way or another, the influence that this hypothesis has had in the field of neuroscience is undeniable.









